Debye-Hückel Theory Explained: Equation, Assumptions, Limitations, and Applications in Electrolyte Solutions
In 1923, Debye and Hückel, and later in 1926, Onsager, proposed the modern theory of strong electrolytes, which considers the role of electrostatic forces between ions.
Main Assumptions of the Debye Huckel Theory
• The electrolyte is completely dissociated, indicating it is a strong electrolyte.
• Ions are assumed to be spherical, and ion solvation is neglected in this theory.
• The solvent does not participate actively; it merely provides a medium for ionic interactions.
• The surrounding ions are treated as an average cloud of continuous charge density around a central ion.
A spherical cloud of opposite charge, known as the ionic atmosphere, surrounds each central ion. This atmosphere carries a net charge equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to that of the central ion. Due to electrostatic interactions with its ionic atmosphere, the energy and chemical potential of the central ion are lowered.
According to this model, at very low concentrations, the activity coefficient of ions can be calculated using the Debye-Hückel limiting law.
Watch Full lecture in Urdu/Hindi
Watch Full lecture in English
Main ideas of the theory is given below :
(1) The strong electrolyte is completely ionised at all dilutions: However, recent studies show that a small amount of unionized substance is present, so instead of saying the electrolyte is ‘completely ionized,’ it is more accurate to say it is ‘almost completely ionized.
(2) Since oppositely charged ions attract each other, it suggests that anions and cations are not uniformly distributed in the solution of an electrolyte but that the cations tend to be found in the vicinity of anions and vice-versa . Though the solution is on the whole neutral, there is in the vicinity of any given ion a predominance of ions of opposite charge which we call as counter ions. The ions are all the time on the move in all directions but on the average, more counter ions than like ions pass by any given ion. This spherical haze of opposite charge is called ionic atmosphere.
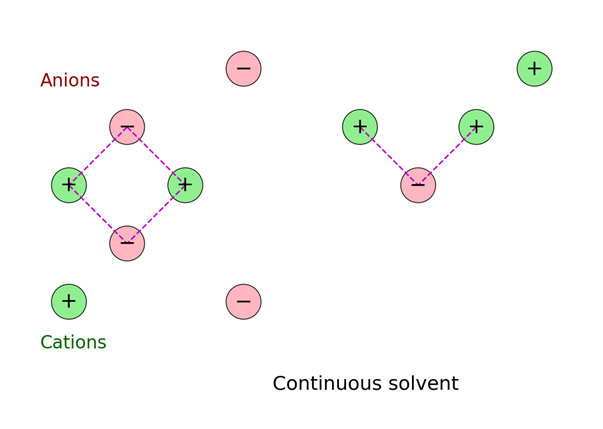
(3) The decrease in equivalent conductance with increasing concentration is due to reduced ion mobility caused by stronger inter-ionic interactions. Conversely, as concentration decreases, ion mobility increases, leading to higher conductance.
(4) The ratio λν / λ∞ does not correctly give the degree of dissociation α for strong electrolytes but only the conductance or conductance coefficient fc.
(4) The ratio λν / λ∞ does not correctly give the degree of dissociation α for strong electrolytes but only the conductance or conductance coefficient fc.
(5) In spite of almost complete ionisation, λν is much less than λ∞.n
Debye-Hückel Theory Visualizer
This ionic atmosphere screens the central ion’s charge, causing the electrostatic potential to decrease exponentially with distance, characterized by the Debye length (λD).
Blue dots = counter-ions (negative charge, attracted), red dots = co-ions (positive charge, repelled), and the large dark blue dot is the central ion.
The Debye-Hückel-Onsager conductance equation accounts for these factors and, for a fully dissociated univalent electrolyte, is expressed as follows:
The Debye-Hückel-Onsager conductance equation accounts for these factors and, for a completely dissociated univalent electrolyte, is expressed as follows: where A and B are constants that depend solely on the nature of the solvent and the temperature, and c is the concentration in gram-equivalents per litre.
Where D and are the dielectric constants and coefficient of viscosity of the medium respectively at the absolute temperature
. The constant A is a measure of the electrophoretic effect with B is that of the asymmetry effect. For water at
with
and
the value of A is 60.20.
Download Complete Notes Below
I'm very happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the…
Proudly Powered By




Leave a Comment